HbA1c tests can be utilized by medical practitioners to identify or monitor certain diseases like pre-diabetes and diabetes. If you are worried about your chances of acquiring diabetes or pre-diabetes, you can use the hemoglobin A1C test. However, you might want to know what exactly it is, how doctors use it to calculate the levels and what it actually says about your health. Here is a detailed guide on HBA1C and the ways to reduce them.
What is HBA1c?
If you are someone with excessive glucose buildup, it automatically attaches to a protein known as hemoglobin in the red blood cells. HbA1c [Hemoglobin A1c] is a blood test utilized to measure the amount of glucose attached to the red blood cells, and it shows the percentage of the red blood cells that contain sugar-coated hemoglobin. It shows the blood sugar levels for the past 2-3 months. It is often utilized to identify diabetes and pre-diabetes and check the efficiency of interventions to control blood sugar. As signs of diabetes and pre-diabetes often go unnoticed, it is helpful to know the A1C level even if you do not possess any threat of acquiring these conditions. 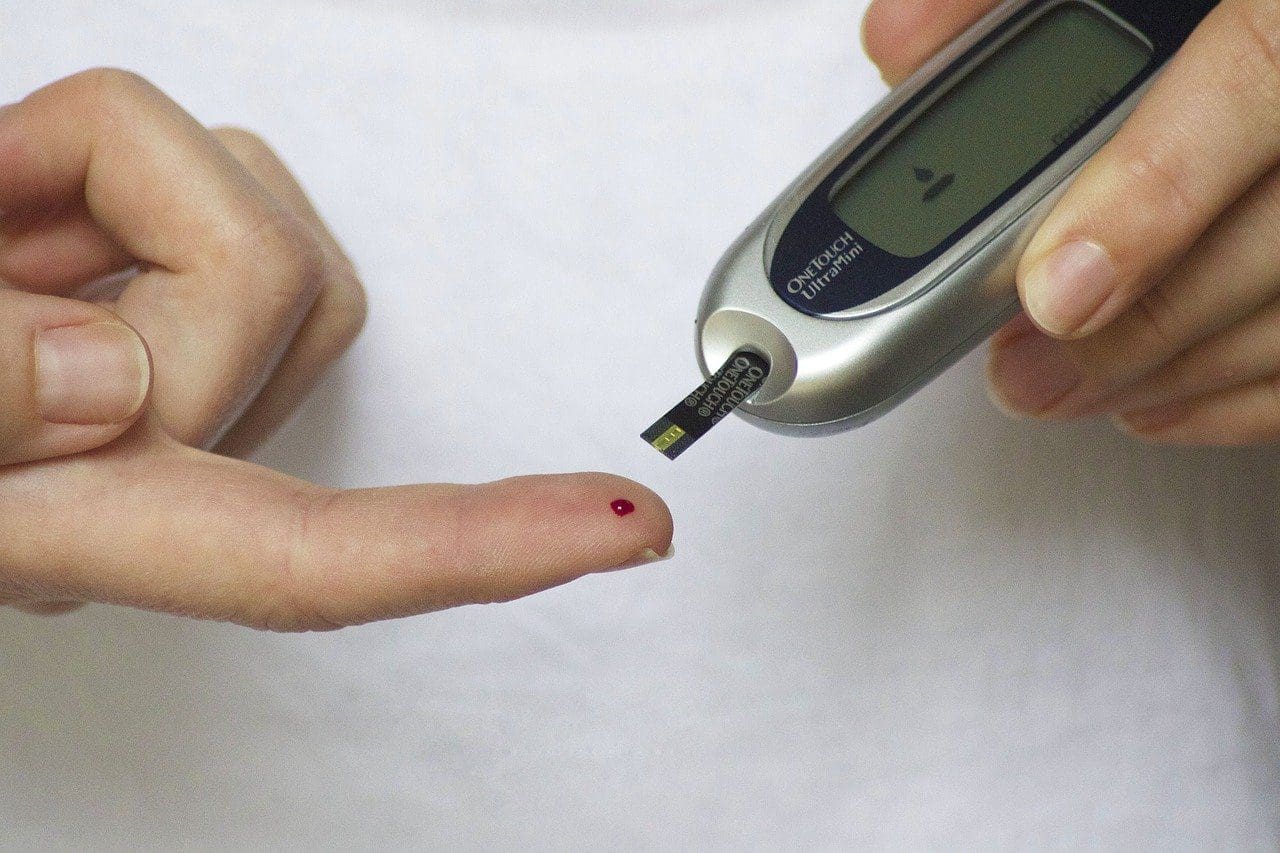
How is this test different from your regular blood sugar finger prick?
To assess the blood glucose or A1C level, the lab technician will do a finger-prick test or take blood from your vein. An A1C test is distinct from a blood glucose test in the following ways.
- A regular blood glucose test notifies you about your current glucose levels.
- An A1C test, on the other hand, offers an average blood glucose level over time. [2 to 3 months, in general]
- Both these tests offer vital information about the ability of your body to regulate blood glucose.
Figuring out HbA1c levels
HbA1c assesses the average blood sugar levels for the last 2 to 3 months. The reading is shown as a percentage. This offers a deep insight into your blood sugar levels and can help ascertain whether your human body is manufacturing sufficient insulin or suffering from insulin resistance.
The following are the HbA1c test result levels.
Optimal: The levels are considered normal if they are below 5.7%. For individuals without diabetes, the standard range is often between 4% – 5.6%.
Elevated: If the levels range from 5.7 to 6.4%, you may be pre-diabetic. This increases your chances of getting type 2 diabetes, stroke, and heart disease.
High: Levels above or at 6.5% are usually a sign of diabetes, and this elevates your threat of stroke, visual impairment, heart disease, kidney disease, neuropathy, and various other conditions.
What influences HbA1c?
Several factors play a significant role in the A1c level, like;
- Diets, especially those high in sugars and refined carbohydrates and low in fiber
- Obese or overweight individuals
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Age (particularly adults who belong to the age group of 45 or more)
- Low HDL cholesterol levels
- High blood pressure
- Stress
- Race (people of Hispanic/Latino, Black, American Indian, Pacific Islander, or Asian American descent are at higher risk for diabetes/pre-diabetes.)
- Certain medications, [glucocorticoids]
- Pregnancy
- Genetics (family history of diabetes or pre-diabetes)
- PCOS

How to reduce HbA1c
You can change your lifestyle habits and diet to have an affirmative effect on your HbA1c levels. Here are specific science-backed ways to help you reduce HbA1c levels eventually.
Focus on nutrition
Studies show that a diet focusing on lean protein, whole grains, plant-based fat, and non-starchy vegetables can considerably help control your blood sugar levels. On the other hand, diets rich in refined sugar and carbohydrates have been shown to boost HbA1c levels, so you need to limit the intake of those foods.
Do some physical activities
Frequent exercise is an excellent way to enhance your A1c. While all types of exercise offer fantastic health benefits, studies show that a combination of aerobic exercise and strength training is more beneficial in reducing HbA1c. To get the advantages, you must do at least 150 minutes of average physical activity per week. You need to check with your physician before starting any exercise regime.
Keep your weight in check
If you are obese or overweight, you need to lose some weight to reduce your HbA1c levels. Research shows that just a 0.1% reduction in your HbA1c level can result in losing 1 kg of your body weight.
Lower your stress and get ample sleep
High-stress levels and inferior sleep quality correlate with increased HbA1c levels and weight gain. Studies show that stress levels trigger a rise in A1c. People who sleep below 5 hours every night have elevated blood glucose levels compared to the ones who sleep over 7 hours.
Consider using a supplement
Some researches show that supplements might aid in controlling your blood sugar. Cinnamon, berberine, probiotics, magnesium, and vitamin D are a few supplements that have helped in reducing A1c and enhancing insulin sensitivity. While supplementation can be a helpful way to reduce A1c levels, they are not a standalone tactic. You must talk to your medical practitioner to see which supplements suit you.


Be the first to comment