Artificial Intelligence is an emerging branch of computer science that deals with designing machines or systems capable of performing tasks usually performed only by humans. AI was first introduced into human life during the past couple of centuries when people used mechanical devices like clocks, calculators, etc., to perform simple calculations.
The term “artificial intelligence” has been coined in 1956 by John McCarthy at Dartmouth College and popularized by his student Marvin Minsky who published a book on this subject titled: Artificial Intelligence—A Modern Approach in 1969. In 1970, Allen Newell and Herbert Simon proposed their famous paper called ‘What Is Machine Learning?’ which laid down some basic principles for developing intelligent agents.
In the 1960s, there was another major breakthrough in robotics when Marvin Minsky proposed his theory about ‘Perceptrons.’ Perceptron was basically a mathematical model designed to mimic how neurons work inside our brain. It was one of the earliest models that attempted to simulate neural networks using digital computers. Later on, many more models followed suit, including Connectionist Models, Rule-Based Systems, Expert System, etc.
This led to the development of many different types of artificial intelligence such as expert systems, neural networks, evolutionary algorithms, genetic programming, fuzzy logic, symbolic reasoning, knowledge-based systems, Bayesian inference, etc.
These techniques have become essential tools in various areas, including medical diagnosis, speech recognition, robotics, natural language processing, data mining, financial analysis, web search engines, games, manufacturing processes, transportation planning, military applications, and many other fields.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
There are two main categories of AI: 1) Machine Learning 2) Deep learning.
Both these techniques have been widely adopted across different industries over the last few years. So let us look at each category separately.
Machine Learning
 This technique involves training a machine to learn from data provided by its environment. For example, if you want your car to drive itself, it needs to understand what driving means. So, before starting off, it will need to collect information regarding all possible situations that might arise while driving. Then, after collecting enough data, it would start teaching itself through experience. Once trained, the system would be able to make decisions automatically.
This technique involves training a machine to learn from data provided by its environment. For example, if you want your car to drive itself, it needs to understand what driving means. So, before starting off, it will need to collect information regarding all possible situations that might arise while driving. Then, after collecting enough data, it would start teaching itself through experience. Once trained, the system would be able to make decisions automatically.
An excellent example of this type of technology is Google Now. For example, if you ask Google Now to give you directions to somewhere, it will analyze your current location, destination, time, day, season, wind speed, temperature, humidity, cloud cover, visibility, moon phase, sunrise/sunset times, nearby landmarks, historical events, political conditions, crime rates, traffic patterns, accident reports, gas prices, recent searches made by others, etc. All this information is collected and analyzed to provide you with accurate predictions about the future.
Another great example of machine learning is Siri. When you say something like “Siri, play music,” she analyzes your voice pattern and plays whatever song you asked her to play. She does not know anything about music; she just learns from your commands.
Deep Learning
 This is a relatively new form of AI. Unlike traditional machine learning algorithms, deep learning uses multiple layers of hidden units. Each layer has fewer connections than the previous ones. As we move deeper down, the number of connections decreases exponentially until finally, we reach the output unit. Deep learning works better than conventional methods because it allows the network to extract features directly from raw input data without any intermediate processing steps.
This is a relatively new form of AI. Unlike traditional machine learning algorithms, deep learning uses multiple layers of hidden units. Each layer has fewer connections than the previous ones. As we move deeper down, the number of connections decreases exponentially until finally, we reach the output unit. Deep learning works better than conventional methods because it allows the network to extract features directly from raw input data without any intermediate processing steps.
An excellent example of deep learning is AlphaGo. It beat world champion Lee Sedol 4-1 in 2016. AlphaGo learned to play Go solely through self-play games against itself. It did not require any external knowledge such as books, videos, tutorials, etc. Instead, it taught itself everything it needed to know about playing Go.
How is AI currently used in dentistry?
It should be emphasized that AI is there to use the data we already have to make predictions, act, and learn.
Artificial intelligence is a rapidly growing field, and dentists are no exception. The use of AI has been steadily increasing over the past few years as it becomes more accessible to dental practices. In fact, according to an article published by Dental Economics, “AI-powered software can be used for everything from patient scheduling to treatment planning.”
AI can help improve patient outcomes through better diagnosis, treatment planning, decision-making, communication with patients, and more accurate documentation. It also has potential applications for improving efficiency and reducing costs.
1) Dentistry has always been a profession where you have to be patient and wait for your turn. But now, there’s no need to worry about waiting as artificial intelligence can help us, schedule patients. It will also make sure we get our appointments on time without any hassle.
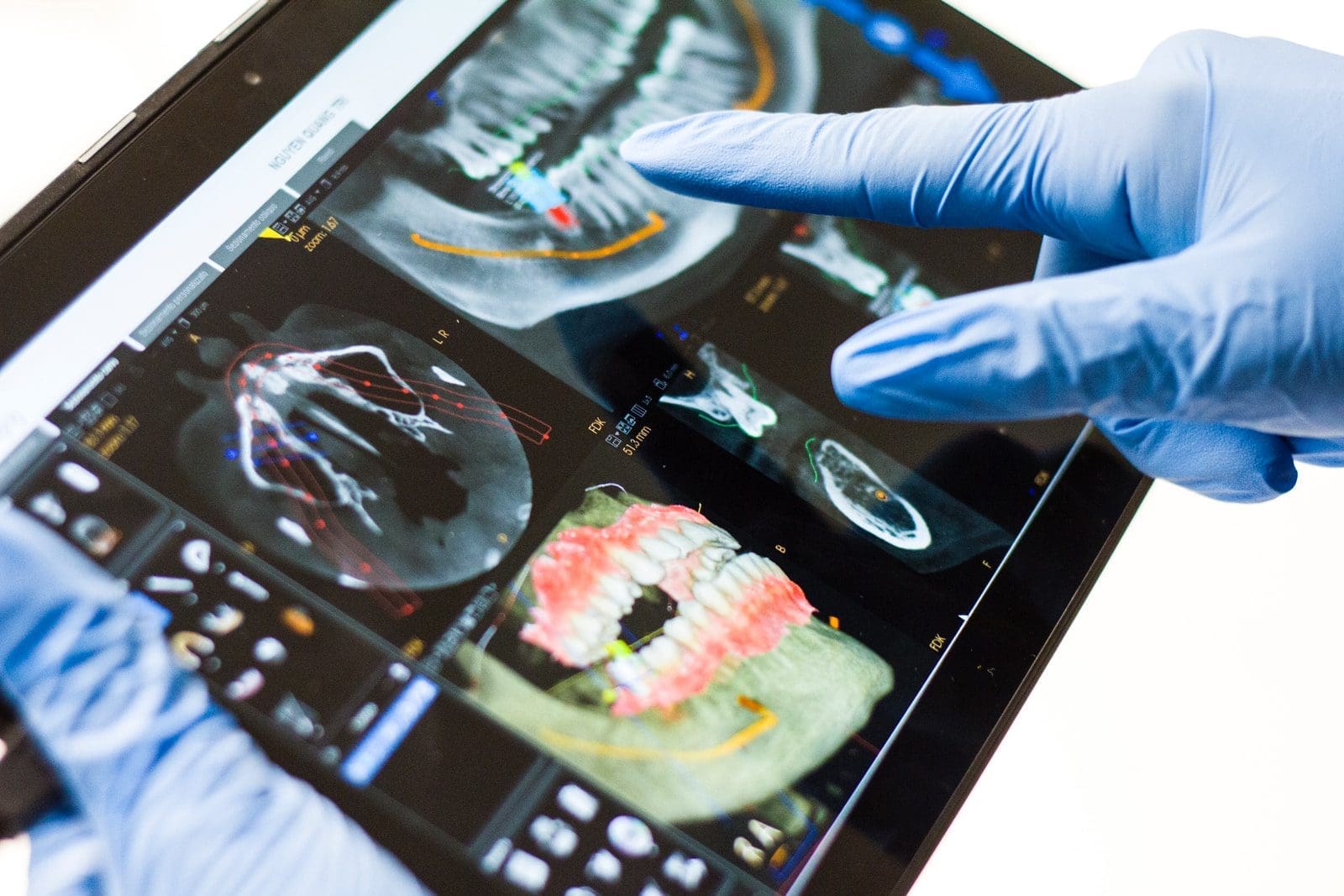
2) Artificial intelligence can also assist dental professionals in diagnosing diseases using images taken from X-rays and other medical imaging techniques. This would allow them to identify problems before they become serious.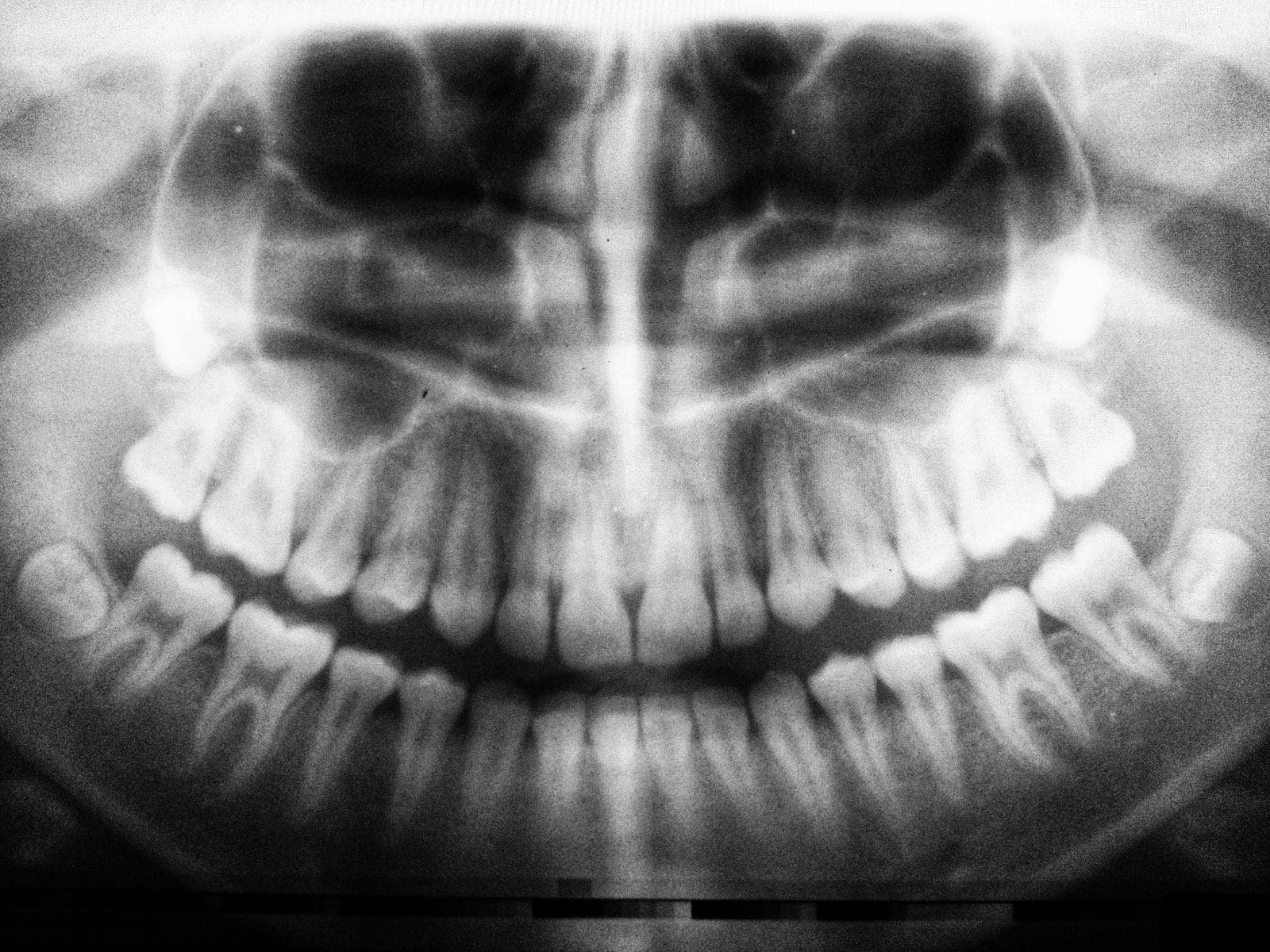
The use of artificial intelligence has been proposed as an alternative method for detecting caries lesions on teeth. The system uses image processing techniques to identify tooth surfaces with white spots indicative of early stages of decay. It then compares these images against previous examinations to determine whether any new areas have developed since the last review. If so, it alerts the dentist, who may decide to perform the further treatment.
3) Another way it could change things around is by improving treatment options available to patients. For example, suppose a dentist diagnoses a toothache but doesn’t know what caused it. In that case, they might suggest filling, which may not necessarily fix the problem because sometimes even minor cavities can lead to more severe issues later.
Oral cancers include squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinomas, melanomas, lymphomas, sarcomas, and other malignancies. Oral cancer screening has traditionally relied upon visual inspections of suspicious tissue or physical examinations. However, this method lacks sensitivity and specificity. In addition, there are many cases where early signs of oral cancer may not appear until later stages. AI can theoretically help provide early detection of various oral lesions and provide appropriate early care to the patients.
4) In addition to these benefits, AI can also provide better services than ever before. For example, today’s technology allows us to record everything happening inside the mouth, including temperature changes, blood flow patterns, pressure points, nerve responses, muscle movements, brain waves, heart rate, breathing pattern, voice inflections, and much more.
With all these advantages, why isn’t everyone already using AI?
So, while AI is slowly becoming mainstream, its full potential hasn’t been realized just yet. We’re only beginning to understand how far it can go.
When will AI reach a tipping point for adoption?
AI is still relatively new, but its potential uses are endless. The question remains whether or when AI will become mainstream. In my opinion, it won’t happen overnight. However, if you’re interested in how AI could impact your practice, now might be an ideal time to start thinking about what you want to achieve.
What do I need to consider when using AI in dentistry?
1) Data – You’ll need lots of good quality data to train your model. Data collection methods vary depending on the type of application being used. Some examples:
- Images.
- Videos.
- Audio recordings.
2) Training set – A training set contains all the information needed to build up your model. Training sets usually consist of labeled samples. However, some models require unlabeled samples instead.
3) Model architecture – How does the system work? This includes the number of layers, types of neurons, activation functions, etc.
What do I need to consider as a practitioner?
1) Ethics & Privacy – It’s essential to think carefully about ethics and privacy when working with any machine learning algorithm. Several different approaches to handling sensitive patient data, such as deidentification, anonymization, encryption, etc.
2) Efficiency – When building a predictive model, efficiency refers to how quickly the model learns from input data. Models that take longer to train tend to overfit the training dataset and produce poor results on test datasets.
3) Scaling – Scaling refers to the ability of a model to handle large amounts of data without losing accuracy. For example, deep neural networks often struggle to scale well because they rely heavily on backpropagation through multiple hidden layers.
How can I improve my dental practices by leveraging AI?
Here are 3 areas where AI has great potential to transform our industry:
1) Patient Experience
The first area where AI can really change things is improving the overall experience of visiting a dentist. With AI, we can automate processes like scheduling appointments, tracking insurance claims, communicating with patients via email/text messages, sending reminders, performing routine exams, diagnosing conditions, recommending treatments, and so forth. These tasks currently involve manual labor, which means they’re slow, error-prone, and expensive. By automating these processes, we can reduce costs while increasing productivity.
2) Productivity
Another way AI can help us increase productivity is by reducing errors during treatment planning. We already use computer-aided design, virtual reality, augmented reality, and other technologies to create digital mockups of teeth before starting procedures. But there are many more opportunities for improvement.
For instance, we could leverage AI to automatically detect tooth decay and recommend appropriate restorative options based on the severity of the condition. Or perhaps we could develop algorithms capable of predicting future problems and suggesting preventative measures.
3) Cost Savings
Finally, AI can also save money by helping us identify cost-effective solutions to common issues. For example, we could use AI to predict the likelihood of developing caries. Then, rather than spending hours manually reviewing x-rays, we could simply send them directly to specialists who would then make recommendations regarding further testing and possible interventions. This approach not only saves time but reduces unnecessary radiation exposure.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence will continue to play an increasingly significant role in transforming healthcare delivery. Dentistry is no exception. As practitioners, we have much to gain from this technology if we choose to embrace it.

Be the first to comment