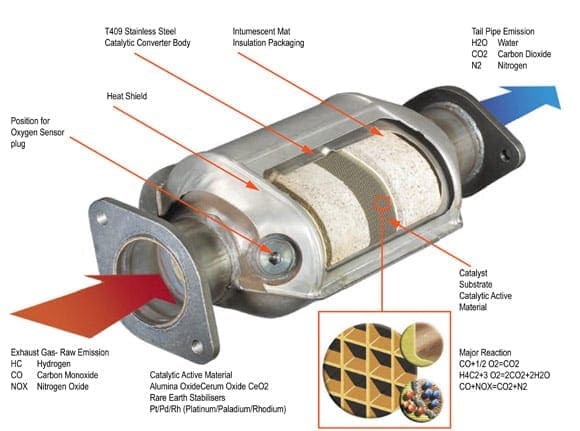
Catalytic converters are devices that control the emissions of internal combustion engines. Internal combustion engines create toxic combustion gases. Using a catalyst to create a chemical reaction, exhaust waste can be converted into harmless gas and water, thereby reducing toxic emissions from the exhaust.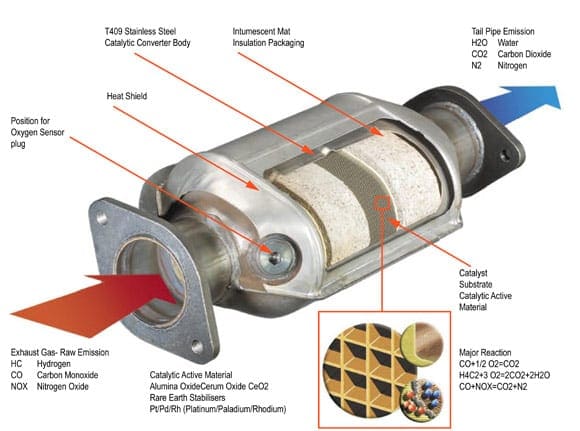
The catalytic converter works with the oxygen sensors and other components of engine management to manage the emissions stemming from the engine. Ceramic substrates are used inside the converter with a special coating of ceria, rhodium, platinum, and palladium. This is a delicate manufacturing process and must be done right as temperatures of 400° Celsius and hotter will blaze through the catalytic converter on a regular basis. When manufactured and installed correctly, the catalytic converter makes a big impact on minimizing the impact of engines on the environment.
Catalytic converters appeared in the automobile market in the United States in 1975. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency had increased its restrictions on emissions testing for new vehicles and manufacturers responded with the catalytic converter. The original version of the catalytic converter was a two-way model, taking carbon monoxide and combining it with unburned hydrocarbons to make water and carbon dioxide. Today’s catalytic converters are three-way models, converting nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and unburned hydrocarbons into nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and water.
In addition to being used for cars and trucks, catalytic converters are also used in locomotives, motorcycles, airplanes, buses, semis, yale forklifts, generator sets, and other devices that use engines. Even some wood stoves use catalytic converters to meet the modern requirements for reduced air pollution from burning.
About the Author: I am John, love to write more about automobiles. For more information on this topic or related topic, click here magnaflow exhaust

Be the first to comment